

Homepage > CMRC understandings > 【CMRC understanding】With the continuous promotion of environmental protection policies, new carbon sources usher in a good opportunity for development, and future commercial use is worth looking forward to!
Hits:3009 Createtime:2022-12-05 14:26:56
With the continuous promotion of national environmental protection policies and the continuous improvement of people's environmental awareness, the requirements for the discharge of treated sewage are increasingly strict, especially the discharge of nitrogen. At present, the common method used by many urban sewage treatment plants or reclaimed water plants is to remove nitrogen by adding carbon sources. The traditional external carbon sources are mainly methanol, sodium acetate, glucose, etc., but the traditional carbon sources have shortcomings of poor safety and high cost, which limit their further development and application. In this context, new carbon sources usher in a good opportunity for development.
1. Definition and classification of carbon sources
Carbon sources are nutrients used to form carbon sources in microbial cells and metabolites. The common classification method in the industry is to divide carbon sources into single carbon sources and composite carbon sources.
Single carbon source: a carbon source containing only one effective carbon source component.
Composite carbon source: a carbon source consisting of two or more effective carbon source components, which must be compatible with each other and free from chemical reaction and safety risk.
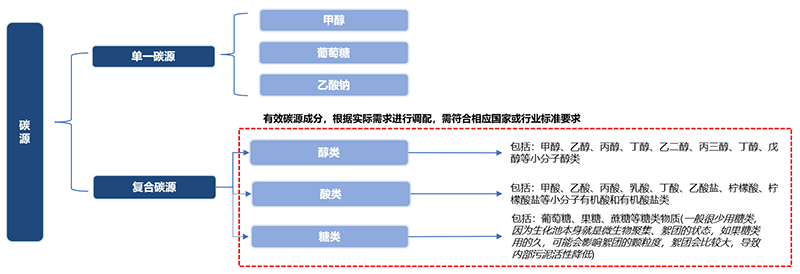
2. Analysis of carbon source industry chain
The whole industrial chain of carbon source includes the whole process of raw material collection and transportation, carbon source processing, transportation and downstream use.
From the perspective of carbon source raw material suppliers, different carbon sources require different kinds of raw materials with diversified sources, but they are basically purchased and rarely produced by themselves.
From the perspective of carbon source production enterprises, due to the low threshold of carbon source production technology and the large number of participating enterprises, they are basically in a state of complete competition. In addition to transportation costs, few carbon source enterprises choose to develop across regions.
From the perspective of downstream users, they are mainly sewage treatment plants (mainly divided into industrial sewage treatment plants, domestic sewage treatment plants, and municipal sewage treatment plants), some reclaimed water plants (equivalent to the upgrading of sewage plants, and the reclaimed water can be used for municipal greening, parks and ponds, etc.), and a small amount of garbage leachate from garbage transfer stations.
3. Factors affecting carbon source selection
According to the CMRC survey, it is found that the influent water quality and wastewater retention time of the water plant will affect the carbon source selection. Among them, the carbon nitrogen ratio is very important for water quality. This indicator is related to the region, water plant type, season and other factors. If the carbon nitrogen ratio is greater than 5, the water plant can not add carbon sources throughout the year. If the carbon nitrogen ratio is less than 5, different carbon sources will be selected according to the actual situation. Take the regional factor as an example: the regional factor mainly affects the domestic sewage, and the carbon nitrogen ratio in the north will be lower than that in the south, mainly because of different living habits. The northern people are used to drinking high protein and fatty foods, so the nitrogen content in the domestic sewage is relatively high, leading to low carbon and nitrogen.

4. Carbon source selection
At present, the most important indicator for measuring various types of carbon sources in the market is COD equivalent (chemical oxygen demand). When treating the same amount of sewage, the higher the COD equivalent of carbon sources, the less the total amount needed to be added. Other indicators include denitrification rate, reaction stability and sludge yield.
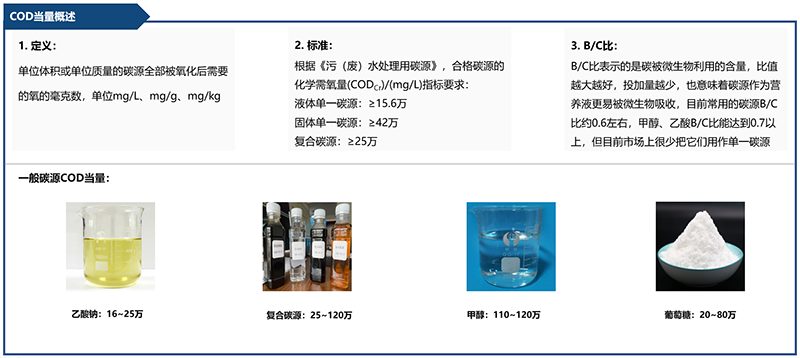
Historically, single carbon source is the product with the longest application, mainly including sodium acetate, glucose and methanol, among which glucose and methanol are relatively less used, especially methanol.
Sodium acetate: from the perspective of economy, the market price of sodium acetate is low, and the price is more expensive under the same COD equivalent; From the use effect, sodium acetate has the fastest reaction rate, good stability and nitrogen removal effect, and the best comprehensive market performance.
Glucose: from the perspective of economy, the price of glucose in the market is expensive and relatively cheap under the same COD equivalent; From the perspective of use effect, glucose sludge has a large output, high sludge treatment cost and few practical applications in the market.
Methanol: from the perspective of economy, the market price of methanol is on the high side, and the price is cheap under the same COD equivalent, so the economy is better; From the perspective of use effect, methanol is single in composition, flammable and explosive, with high safety risks and few practical applications.
In general, there is no standard product in the composite carbon source market, which is formulated according to customer needs. From an economic point of view, the composite carbon source makes full use of the advantages of the main components, including the high COD of small molecule alcohols, the high reaction rate of sodium acetate, and the high microbial absorption of sugar. The result is that the concentration of organic matter is relatively high, the COD equivalent is relatively large, and the overall measurement results in a significant reduction in the dosage, and also reduces the cost of transportation, unloading, and storage tank facilities. The comprehensive cost is low, and the cost performance is high. From the perspective of use effect, the nitrogen removal effect is good, and the reaction rate is in the middle. Although the stability is weaker than that of a single carbon source (it does not affect the use, and only needs to be tested before each batch is used), the composite carbon source can be used by denitrifying bacteria in biochemical sludge, not by microorganisms such as filamentous bacteria that cause excessive sludge growth, and the sludge production is relatively small.
5. New carbon source
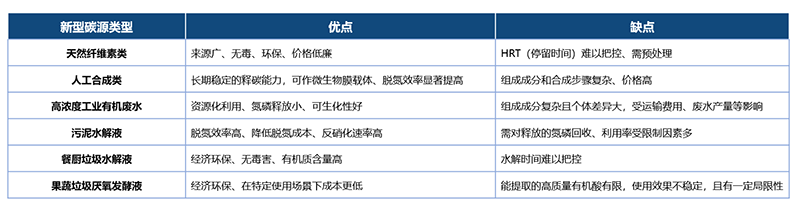
The new carbon sources can be divided into solid carbon sources and liquid carbon sources according to the physical state, of which the solid carbon sources include natural cellulose carbon sources, artificial synthesis solid carbon sources, etc; Liquid carbon sources include high concentration industrial organic wastewater, sludge hydrolysate, kitchen waste hydrolysate, fruit and vegetable waste anaerobic fermentation liquid, etc.
Under the influence of the new sewage treatment concept, the new carbon source with high efficiency, environmental protection and low cost has become the current research focus of universities and manufacturers. The new solid carbon source is difficult to control and has high cost. The new liquid carbon source represented by high concentration industrial organic wastewater, sludge hydrolysate, food waste hydrolysate, and fruit and vegetable waste anaerobic fermentation liquid can not only remove nitrogen efficiently, but also conform to the concept of waste resource reuse. However, there are still some problems that restrict its wide commercial use, Therefore, the research focus of new carbon sources in the future will be more on how to widely commercialize.
summary
There are more or less problems with the traditional carbon sources currently used. With the promotion of environmental protection policies, sewage discharge requirements are increasingly strict; With the impact of the epidemic and the economic downturn, manufacturers have to control costs, so there is an urgent need to use a new type of carbon source that is more environmentally friendly and economical at present and in the future. Although most of the existing new carbon sources are still in the laboratory stage, and there are still various problems in practical application, they have the advantages of environmental protection, low cost, and research has been making progress. It is worth looking forward to when they can be large-scale commercial in the future.