

Homepage > CMRC understandings > 【CMRC understanding】With the increase of hydrogen demand, PEM hydrogen production may become the focus in the future.
Hits:2264 Createtime:2022-11-07 13:51:05
Fuel cell vehicles are growing rapidly, and the demand for hydrogen continues to increase.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are one of the most direct and effective ways to apply hydrogen energy. In recent years, China's hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have grown rapidly. Although affected by the epidemic situation, the production and sales of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles will decline in 2020 and 2021, but with the use of demonstration vehicles for the Winter Olympics, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles will gradually be accepted by the market. In addition to the launch of the city cluster of demonstration application of fuel cell vehicles, the production and sales of both vehicles are expected to exceed 4000 this year, And continue to grow upward. In 2021, the production and sales of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles will be dominated by bus heavy trucks, and the number of licensed passenger vehicles will be less than 20. Since this year, the fuel cell passenger vehicles previously deployed by Dongfeng, Chang'an, GAC, SAIC and other major automobile manufacturers have successfully entered the announcement. It is expected that passenger vehicles will continue to grow together with commercial vehicles in the next five years to promote the continuous growth of fuel cell vehicle ownership. It can be expected that the demand for hydrogen gas will also continue to expand in the future.
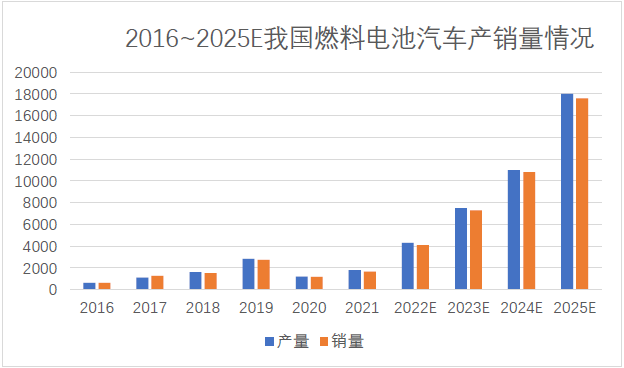
Data source: data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and CMRC's sorting forecast.
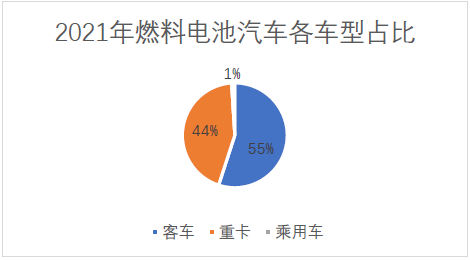
Data source: statistics of compulsory traffic insurance coverage and CMRC sorting.
The growth of downstream demand also drives the continuous improvement of hydrogen production. In 2021, China's hydrogen production will reach 33 million tons, ranking first in the world. At present, hydrogen in China is mainly used in chemical production such as synthetic ammonia, synthetic methanol and petroleum refining. The hydrogen consumption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is less than 1% of the output. However, with the increase of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, the demand for hydrogen in the downstream will continue to increase, and the requirements for hydrogen production, storage and transportation, hydrogenation and other infrastructure construction will also gradually increase. It is estimated that by 2030, the annual hydrogen demand of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles will exceed 2 million tons, and the output value of the production, storage, transportation and processing related industrial chain brought about by hydrogen used by hydrogen fuel cell vehicles will reach the trillion level, and hydrogen used by hydrogen fuel cells will also occupy a more important position in hydrogen use.
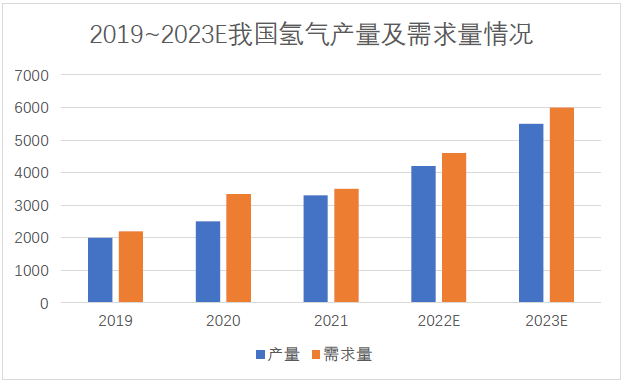
Data source: China Coal Industry Association, CMRC.
"Green hydrogen", a future oriented hydrogen production method
"Green hydrogen" refers to the hydrogen production method using renewable energy for power generation, such as photovoltaic power generation, hydropower generation and wind power generation, to produce hydrogen by electrolysis of water, which achieves zero emission in the whole process of hydrogen production, as opposed to "gray hydrogen" and "blue hydrogen". The so-called "gray hydrogen" refers to hydrogen production from fossil fuels, which will produce a large number of greenhouse gases; The so-called "blue hydrogen" refers to a hydrogen production method that uses carbon capture technology to capture and fix greenhouse gases generated in the production process of "gray hydrogen" and reduce carbon emissions of "gray hydrogen". Among various hydrogen production methods, "gray hydrogen" has the lowest price and is the most widely used hydrogen production method at present. In the future, "green hydrogen" will gradually replace "gray hydrogen" as the main hydrogen production method
At present, although the hydrogen production technology by electrolysis of water in China has been relatively mature, due to the price advantage of hydrogen production by fossil fuels, China still focuses on hydrogen production by fossil fuels in the hydrogen production field, accounting for more than 80%, including 62% by coal and 18% by natural gas, compared with less than 1% by electrolysis of water. In the future, with the implementation of the goals of "carbon peaking" and "carbon neutralization", the mature price of hydrogen production from electrolytic water will decline, and the proportion of hydrogen production from fossil fuels in the hydrogen production field will gradually decrease. Hydrogen production from electrolytic water, especially the hydrogen production from electrolytic water relying on renewable energy power generation, will be the main hydrogen production method in the future.
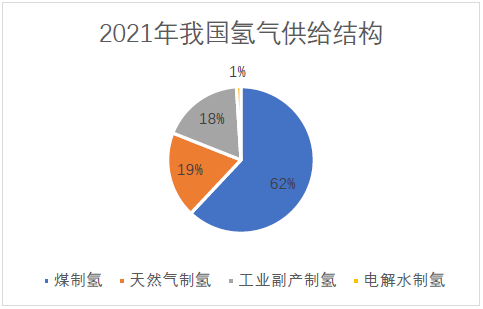
Data source: China Hydrogen Energy Alliance, CMRC
PEM has huge potential for hydrogen production, and the integration of production, storage and processing has become a growth point
After more than 30 years of technological development, at present, China's hydrogen production technology from electrolyzed water mainly includes alkaline electrolyzed water (AE) and proton exchange membrane electrolyzed water (PEM). Among them, alkaline water electrolyzed water (AE) is the largest, accounting for nearly 90% of the scale of hydrogen production from electrolyzed water, while proton exchange membrane electrolyzed water (PEM) only accounts for about 10%; Other new hydrogen production methods such as anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEM) and solid oxide water electrolysis (SOEC) are still in the laboratory stage and have not been put into the market.
Among the two main hydrogen production methods of electrolytic water, the AE hydrogen production unit can achieve more than 1000 standard cubic meters with relatively low cost, which is suitable for large-scale hydrogen production. Due to its slow response speed, it is more suitable for stable power sources such as thermal power generation; And PEM hydrogen production is the most suitable green hydrogen production mode at present due to its rapid response capacity and the instability of renewable energy power generation. At present, PEM hydrogen production is mostly of less than 50 standard m3, and the largest single electrolytic cell can only reach 150~200 standard m3, and the price is several times that of the AE hydrogen production unit of the same standard, which restricts large-scale hydrogen production. However, it is precisely its miniaturization that makes PEM hydrogen production naturally adapt to the demand of distributed energy and integrated hydrogen refueling station, which is also one of its main growth points in the future.
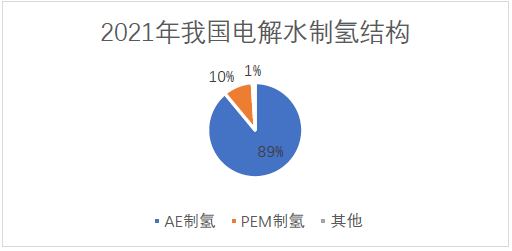
Data source: CMRC interview
epilogue
To sum up, CMRC believes that in the future, with the implementation of the goals of "carbon peaking" and "carbon neutralization", the hydrogen industry will be fully developed, the demand for hydrogen will gradually increase, and higher requirements for hydrogen production will be put forward. At the same time, the choice of hydrogen production methods will also be more low-carbon and environmentally friendly, so green hydrogen will play an increasingly important role in the future hydrogen supply structure. In green hydrogen, proton exchange membrane hydrogen production from water electrolysis (PEM) has shown strong potential in hydrogen production from water electrolysis due to its good combination with renewable energy.