

Homepage > CMRC understandings > 【CMRC understanding】Characteristics of pesticide industry in China
Hits:4395 Createtime:2022-08-12 13:53:25
China's pesticide industry has obvious market characteristics, mainly including:
1. Industry periodicity
Pesticide is a necessity of agricultural production, with small demand elasticity and strong rigid demand. Therefore, it is less affected by macro-economy and belongs to a weak cyclical industry. After the outbreak in 2020, the restoration of domestic and foreign grain prices will drive the return of planting profits. In addition, the policy attaches importance to food security and the recovery of crops and grain sown area will drive the increase of pesticide demand. In the future, the annual output of pesticides will show a stable upward trend.
2. Industry regionality
China's pesticide production has obvious regional characteristics. The production area is mainly concentrated in East China, where many provinces with large output have been attacked. Among them, Jiangsu, Sichuan and Shandong occupy the top three places in domestic pesticide production. In 2021, the pesticide output of Jiangsu, Sichuan and Shandong will be 549 thousand tons, 308 thousand tons and 292 thousand tons respectively, accounting for 22%, 12.3% and 11.7% of the national total.
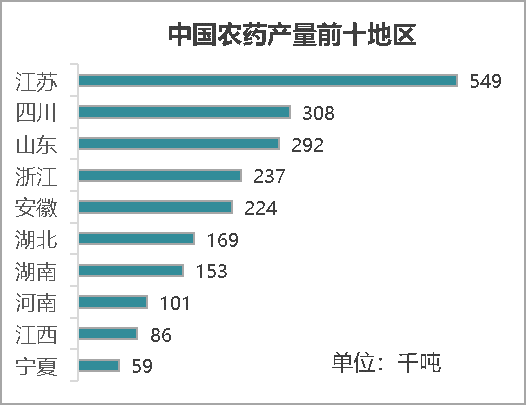
Figure 1 top ten regions of pesticide production in China
The output of East China accounts for 44% of the national output, of which Jiangsu Province is the first (accounting for 49%), Zhejiang Province and Anhui Province are almost the same, ranking the second (accounting for 21%), Jiangxi Province is less (accounting for 8%), and Shanghai is the least (accounting for 1%).
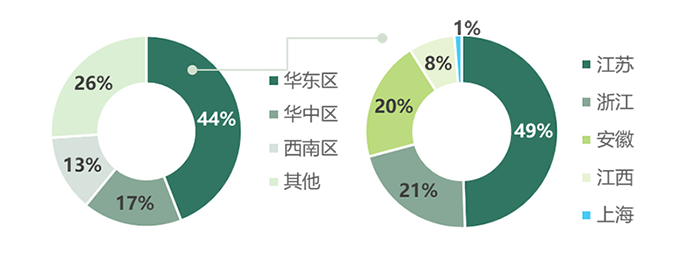
Figure 2 proportion of pesticide output of provinces and cities in East China
3. Industry seasonality
Affected by the seasonality of agricultural production, the production and consumption of pesticides also show obvious seasonality. In China, the first and second quarters of each year are the peak of pesticide production and sales, and the second and third quarters are the peak of pesticide use. The time other than the above seasons is generally the low season for pesticide demand. From the perspective of the global market, the seasonality of the single market is obvious, but the seasonal effects of different markets can offset each other due to the differences in the seasons and natural conditions in the northern and southern hemispheres. The seasonality of the global market as a whole is not obvious.